IVF After Tubal Ligation – Procedure, Recovery & Side Effects
Conceiving naturally after tubal ligation is quite uncommon. But you want to start your family and are worried if there is anything that can help you. In this situation, Assisted Reproductive Technology comes to the rescue. IVF is seen as a promising treatment option to get pregnant after tubal ligation. Also, if a woman conceives naturally, the risk of ectopic pregnancy is quite high.
When the fertilized egg does not get implanted in the uterus but outside it, then this pregnancy is known as an ectopic pregnancy. An ectopic pregnancy can be life-threatening and warrants urgent medical intervention.
So, after tubal ligation, natural pregnancy is not the best option. The best thing to do is to schedule an appointment with a health provider to navigate through all the available options to conceive.
Meanwhile, you can go through this article to understand how IVF after tubal ligation can be a good option. We are going to look at its procedure, recovery, and side effects, if any.
What is Tubal Ligation?
A tubal ligation is a surgical procedure in which the fallopian tubes are cut or tied off, rendering the woman sterile and preventing her from becoming pregnant. Fallopian tubes play a vital role during pregnancy because they transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus, where sperm may fertilize it to form a zygote.
After a tubal ligation, the tubes are mechanically blocked, making it nearly impossible for the egg to become fertilized in the fallopian tube, get implanted in the uterus, and become pregnant.
You are not the only one who wants to have a baby after tubal ligation. Ten to fifteen per cent of women who had their tubes tied later wish to become pregnant again for various reasons, such as going through a miscarriage or marital problems like remarriage.
Why IVF after Tubal Ligation?
When tubal ligation, which involves the tying up of the fallopian tubes, is carried out, In vitro fertilization can be extremely beneficial.
However, IVF after tubal ligation is not the only option.
One of the most invasive procedures for fallopian tube tie-ups is reverse surgery. However, the fallopian tubes don’t need to be reconnected when using IVF for this purpose, and the procedures are non-invasive.
IVF Procedure after Tubal Ligation
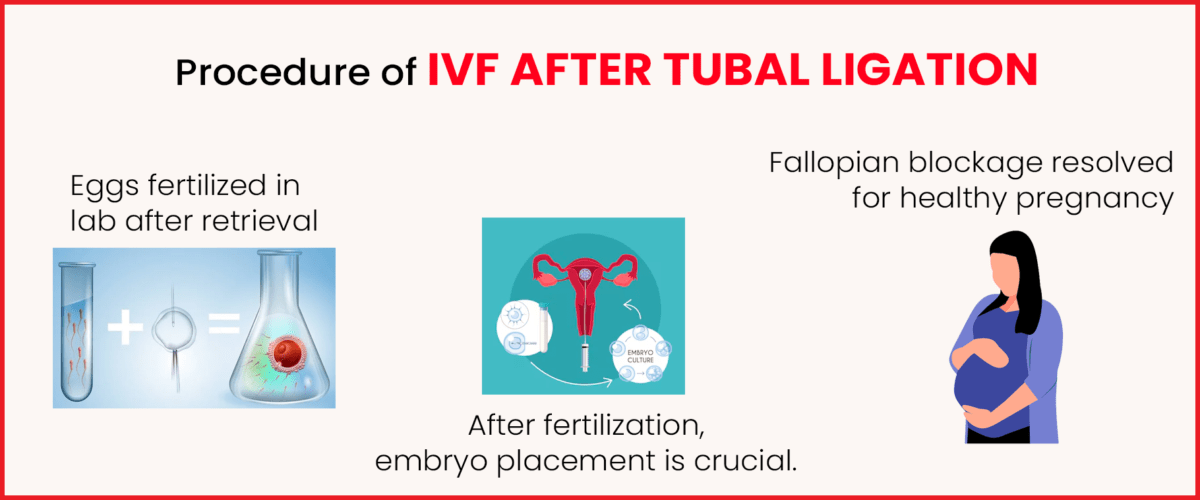
To fertilize in glass is the meaning of In vitro fertilization. Let us discuss in brief how using a specialized IVF procedure can help you get pregnant.
- The woman’s produced eggs are taken straight from her ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a carefully monitored laboratory setting.
- Following fertilization, the patient is consulted regarding the results of the embryos before they are ultimately placed inside the woman’s uterus.
- In this manner, the fallopian tube blockage issue can be resolved, and a healthy pregnancy can be achieved.
Tubal Ligation Reversing V/S IVF.
The highly invasive procedure known as tubal ligation reversal necessitates hospitalization and a protracted recuperation period. Depending on the type of tubal ligation that was performed, the recovery period following these procedures can range from one to two weeks. This phase typically calls for a great deal of pain tolerance, prolonged post-operative care, and patience.
Surgery is not required for IVF treatments in 99 per cent of cases. These treatments seldom leave scars on your reproductive organs and cannot harm them thanks to less invasive methods and drugs. Following IVF, recovery takes less than two days.
Premenstrual symptoms are typically the procedure’s side effects, and they are easily assisted.
Success Rates of Tubal Reversal
Tubal reversal success rates are lower
Many factors affect the success rates of tubal ligation reversal.
Suppose there are no other infertility concerns for the woman. Tubal ligation is unable to address additional fertility problems if the lady is under 40. According to statistics, the success rates of reversed tubal ligation are twice as low for women over 40 as they are for IVF patients. The success rates of the two methods are comparable for 100% fertile women between the ages of 35 and 40. 42–69% of women who undergo reversal surgery go on to become pregnant. However, the success rate of IVF is more promising. Several factors, including general health, fertility history, and the particular tubal ligation technique employed, influence IVF success rates.
In some circumstances, the cost of reversing a tubal ligation may be more than that of an IVF procedure. For instance, a reverse tubal ligation procedure may be more expensive for women over 40 than an IVF procedure.
Ectopic Pregnancy Risk
One possible reason why a reversed tubal ligation pregnancy is not safe is because of the development of an ectopic pregnancy. Up to 3% of women who underwent reverse tubal ligation were reported to have experienced ectopic pregnancy. Indicates that the fertilized egg implants, typically in a fallopian tube, outside the uterus. Ectopic pregnancies can be dangerous, and treatment must start right away. Fainting may occur from internal bleeding, and the fallopian tube may also rupture because of an ectopic pregnancy. Such an incident is not prevalent in IVF.
IVF treatments can be combined in a variety of ways. These are the following:
- The sperm and eggs of the woman’s partner
- Donor sperm and woman’s eggs
- IVF using the partner’s sperm, donor eggs, and the woman’s eggs
- The sperm of the woman’s partner and donor eggs
- Both donor sperm and donor eggs
The fertility examination is the stage at which, typically, the best course of action is suggested in light of the findings. The next step is ovarian stimulation with the right medications if all the examinations that are part of this evaluation are routine.
The most crucial step in treating tubal ligation is retrieving the eggs and sperm. During the retrieval of a woman’s reproductive material, she is lightly sedated and remains unconscious during the entire process. With the use of ultrasound-guided aspiration, the physician extracts the eggs from the ovaries. It takes roughly 20 minutes to complete this process, and it can successfully collect multiple eggs.
Fertilization takes place in a carefully monitored laboratory setting using intracytoplasmic sperm injection external to the woman’s body. Following fertilization, the embryos are allowed to mature to a specific point before their quality is closely assessed. The patient is consulted regarding the number and types of embryos to be transferred before the final transfer.
Potential Risks
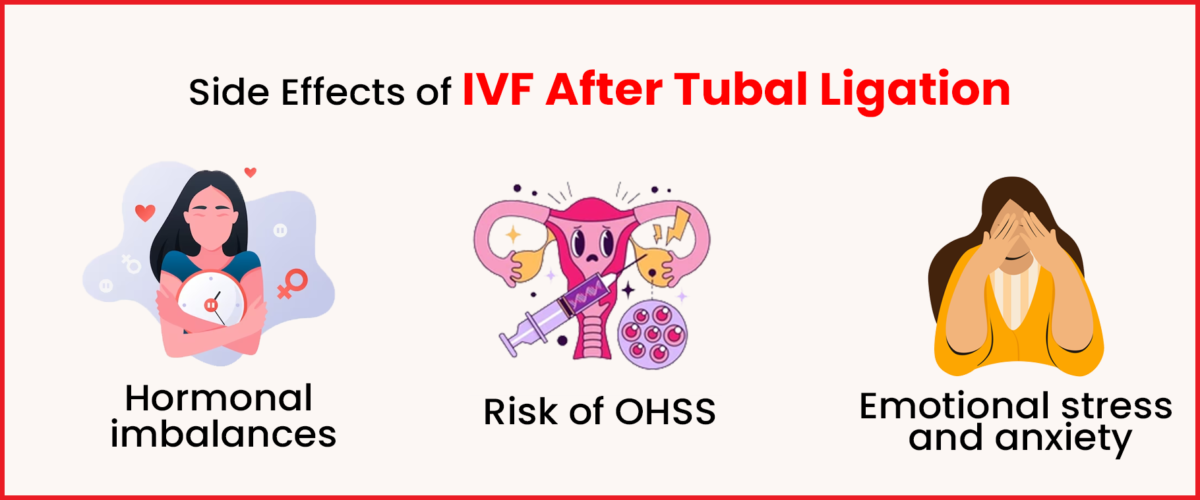
Embryos that successfully implant into two or more pregnancies present unique risks and challenges. Furthermore, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is a possible side effect that has to be closely watched for and managed. Knowing about these possible obstacles enables you to approach the process with preparedness and reasonable expectations.
The likelihood of a tubal ligation reversal operation failing increases with shorter remaining fallopian tube length, advanced maternal age, thermal injury to the tubes, scarred tubal tissue, and inexperienced surgeons. IVF is ultimately the best and last option for these patients whose reversal operation failed.
The decision to undergo tubal ligation reversal surgery or pursue IVF following tubal removal ultimately comes down to personal preferences, medical advice, and circumstances.
Final Words
It is important to see a fertility specialist and obtain medical advice before starting the IVF process after tubal ligation. They will assess your particular situation and offer tailored advice. We’ll perform tests and medical examinations to evaluate your general health, hormone levels, and reproductive health. The fertility team can create a treatment plan that is appropriate and customized to meet your individual needs, thanks to this comprehensive evaluation.
Visit Imprimis IVF for the best IVF treatment. Our committed team of infertility experts is here to offer you thorough information, individualized counselling, and sympathetic support.