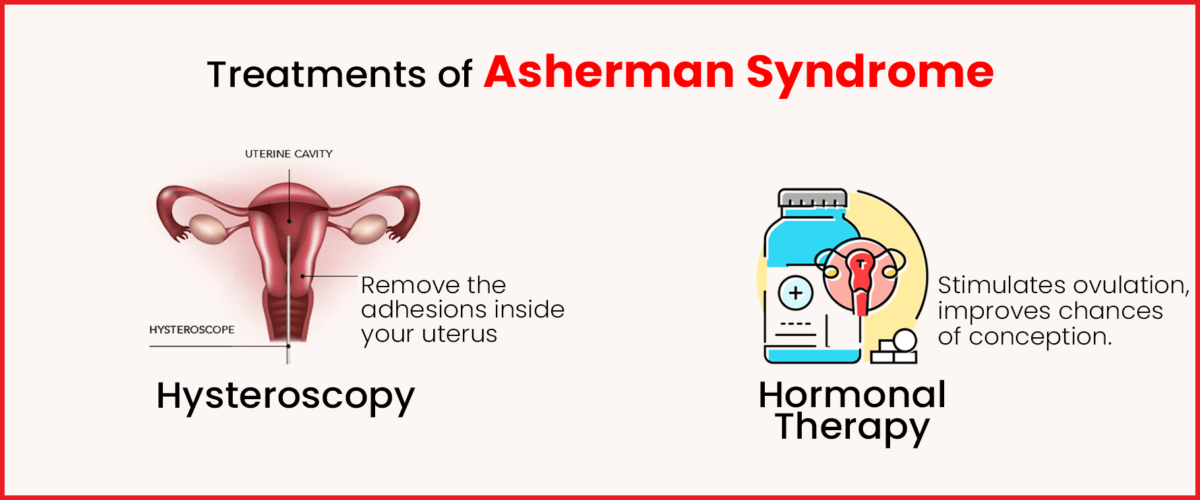
Signs and Symptoms of High Estrogen in Females – Causes & Treatment
Maintaining a proper balance of estrogen and other sex hormones is crucial for overall health. In females, high estrogen levels may result in weight gain, low mood, and severe premenstrual syndrome (PMS). While estrogen is primarily known as a female sex hormone, it’s also present in males, though in smaller amounts. Although estrogen levels naturally fluctuate, consistently high levels can lead to health issues, with effects varying between males and females. But in this article, we will focus only on high estrogen in females.
Keep reading to discover more about the symptoms and causes of high estrogen levels in females.
What is the Meaning of High Estrogen?
Estrogen plays an important role in the human body by regulating key functions like the reproductive system. This hormone’s levels change throughout a person’s life, frequently coordinating with other important chemicals in the body. As a young person goes through puberty, estrogen rises significantly to spur sexual maturation. Working with progesterone, estrogen prepares the body so that it is ready for potential pregnancy later on. Its fluctuations signal important developmental stages from childhood to adulthood. While its levels and impacts vary over time, estrogen remains vital for overall health and well-being at every stage of life.
While a proper balance of hormones is necessary for overall health and well-being, too much or too little of certain hormones can potentially lead to difficulties. Specifically, when estrogen levels are higher than normal for an extended period, it can negatively impact reproductive processes within the body, bring about unpleasant sensations, and elevate the likelihood of developing select health problems. Further exploration into maintaining hormonal equilibrium is advised to avoid potential issues.
What are the Causes of High Estrogen?
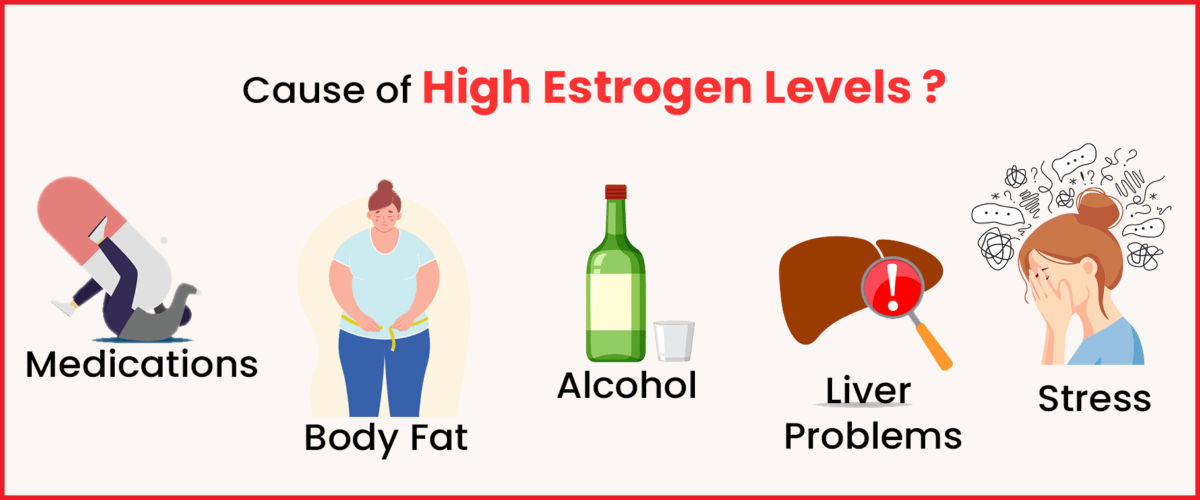
There are a few ways that high estrogen levels can arise in the body. Sometimes, estrogen amounts increase naturally as part of the regular hormonal cycles. However, elevated estrogen may also develop due to certain prescription drugs or underlying medical problems. Some potential causes of high estrogen include:
- Changes in hormones during menopause or the menstrual cycle can cause estrogen levels to fluctuate. The monthly cycle, in particular, experiences surges and drops in various hormones as an egg is selected and developed each month.
- Some medications can raise estrogen in the body. It’s important to be aware of any drugs’ effects on hormone balance.
- Certain underlying medical conditions may contribute to high estrogen. Pregnancy, obesity, ovarian or adrenal tumours, and liver disease from cirrhosis can all impact hormone production and removal from the bloodstream.
- Aspects of one’s lifestyle and habits could play a role as well. Stress, ageing, body weight, and alcohol intake have all been examined for their potential ties to estrogen balance.
- An imbalance between beneficial and harmful bacteria in the gut may slow the liver’s usual elimination of estrogen from the body. A disrupted microbiome could influence hormone processing.
- An overgrowth of problematic intestinal bacteria or a lack of helpful gut microbes may hinder how quickly the liver breaks down and excretes estrogen. Proper gut health supports overall endocrine function.
- Some perfumes and fragrance scents contain chemicals that disrupt typical hormone signalling in studies. More research is still needed, but certain synthetic compounds may disrupt balances.
What are the Signs of High Estrogen?
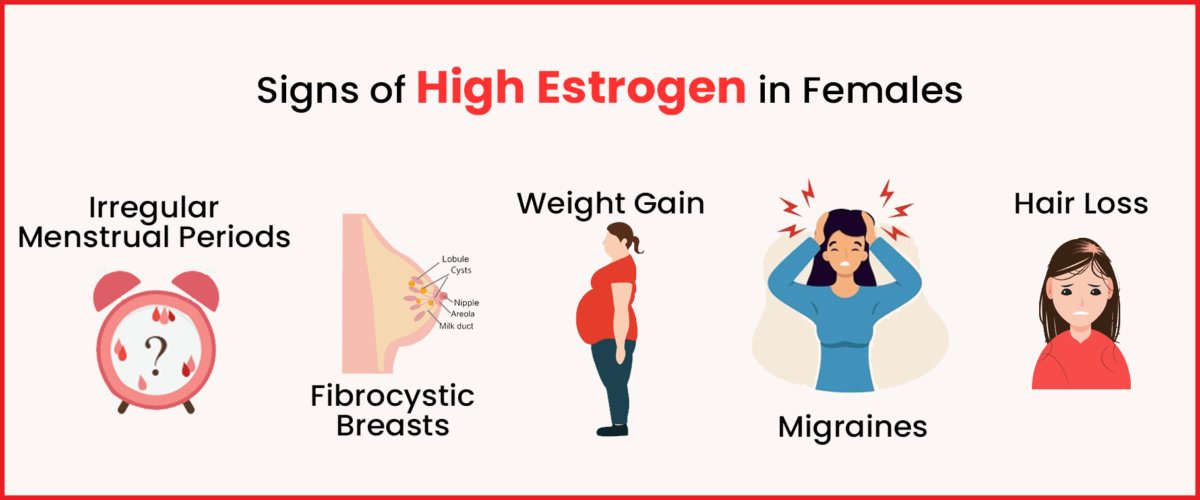
Now that we understand what causes high estrogen in women let’s explore how the body responds to it. Here are some symptoms of high estrogen:
- Abdominal bloating
- Swelling or formation of breast lumps
- Increased breast tenderness
- Irregular periods
- Decreased or absent sexual desire
- Anxiety, panic attacks, or mood swings
- Intensified premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms
- Fatigue, headaches, or tiredness
- Weight gain
These signs illustrate what happens when estrogen levels are high in females. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s wise to consult a doctor and undergo a check-up. Doctors typically recommend a blood test to assess estrogen levels in the body. There’s also a possibility of abnormally low estrogen levels, so it’s essential to get checked.
Diagnosing High Estrogen in Females
If your doctor suspects a hormonal imbalance, they’ll diagnose the cause from your symptoms and specific tests. If hormone replacement therapy (HRT) is causing your symptoms, they might suggest adjustments to your treatment plan.
How to Treat High Estrogen?

Controlling estrogen dominance is crucial to prevent the medical complications mentioned earlier. Here are the most common treatments prescribed by doctors:
Lifestyle changes:
Making lifestyle adjustments can effectively regulate estrogen levels in the body. Consider the following:
● Reduce alcohol intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can hinder estrogen elimination, so it’s best to cut back.
● Opt for healthy, nutritious foods: Eating fibre-rich foods and minimizing processed sugars aids in efficient estrogen breakdown by the liver. Avoiding high-fat meals can also be beneficial.
● Manage stress: While avoiding stress entirely is challenging, learning to cope effectively can promote overall health. Minimizing unnecessary stress helps balance cortisol, estrogen, and progesterone levels.
Medications:
If you’re taking medications for cancer or other conditions, inform your doctor. They can adjust your treatment plan if any medications elevate estrogen levels, especially if you have conditions like cancer that can worsen with high estrogen levels.
Surgeries:
For females at high risk of ovarian or breast cancer, doctors may recommend oophorectomy, the surgical removal of both ovaries, to reduce estrogen production. Another option is ovarian radiation therapy, which halts ovarian function and estrogen production. These procedures do not increase cancer risk or spread.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal estrogen levels in both men and women is essential since this hormone controls multiple body functions. High estrogen levels may bring about a variety of symptoms such as weight gain, mood swings and abnormal menstrual cycles. The development of the factors, symptoms, and diagnosis of high estrogen must be a crucial step in the successful treatment.
Lifestyle factors like limiting alcohol consumption and managing stress can help regulate estrogen levels, whereas medicines or surgical procedures may be required in certain cases. Prompt and comprehensive management of elevated estrogen levels will help to prevent the associated health conditions and guarantee good health. Frequent observation and engagement of healthcare professionals are central to the development of treatment plans specifically geared to suit each person’s needs.