Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) is an overstimulated reaction that often occurs in the ovaries of women who use injectable medications to increase hormone production. This problem leads to severe pain caused by inflammation of the ovaries.
Women undergoing IVF or ovulation stimulation by using injection medications may manifest this OHSS. This article will focus on better understanding what OHSS is, its causes, its symptoms, and how to treat it.
What is Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
OHSS, or Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, occurs when the ovaries swell and release fluid into the abdomen. This complication typically affects individuals undergoing fertility treatments that stimulate their ovaries to produce more eggs.
Usually, a woman who is menstruating only releases one egg monthly. Consequently, women who are going through fertility treatment might have to undergo hormone therapy for hyperovarian activity, especially during the egg retrieval process of IVF. Due to the ovaries’ hyper-response to those medications, it eventually leads to OHSS. This happens often with the medicines that are injected and activate the ovaries more frequently.
While OHSS used to be a common complication of IVF, new protocols have reduced its occurrence, although mild cases still arise occasionally.
OHSS is more prevalent in individuals undergoing fertility treatments who have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition characterized by hormonal imbalances. It’s also more common in those with a high egg supply.
Primary Causes of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
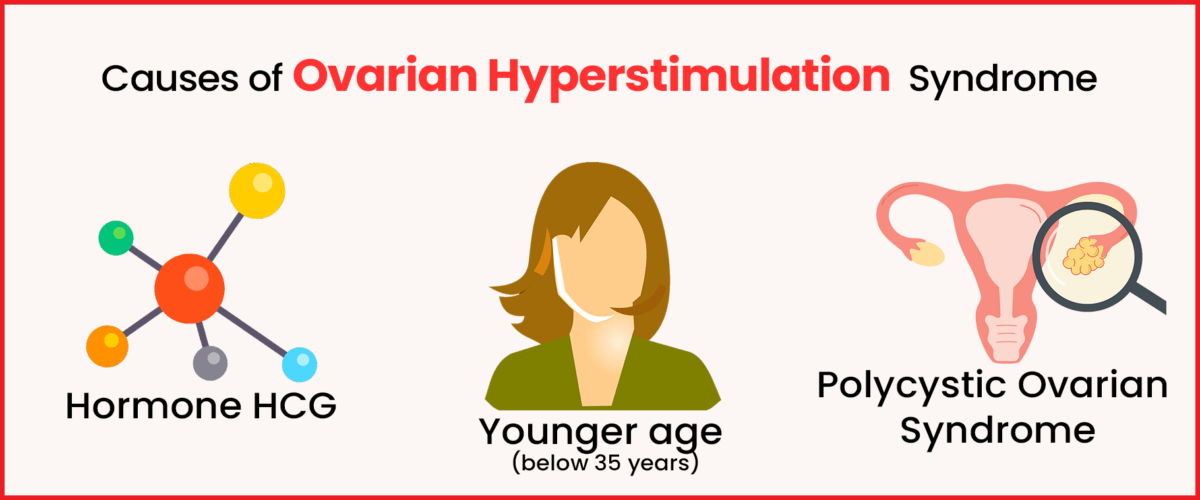
OHSS is primarily triggered by the hormone HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), which stimulates the ovaries. While ovaries typically release one egg, hormone treatments prompt them to produce multiple eggs simultaneously. During fertility treatments, individuals often receive an HCG “trigger” to help egg maturation before in vitro fertilization’s egg retrieval process. Excessive response to this medication can lead to OHSS.
In OHSS cases, fertility drugs cause blood vessels surrounding the ovaries to leak fluid. This fluid may enter the abdomen, resulting in symptoms like swelling and pain.
What are the Symptoms of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome?
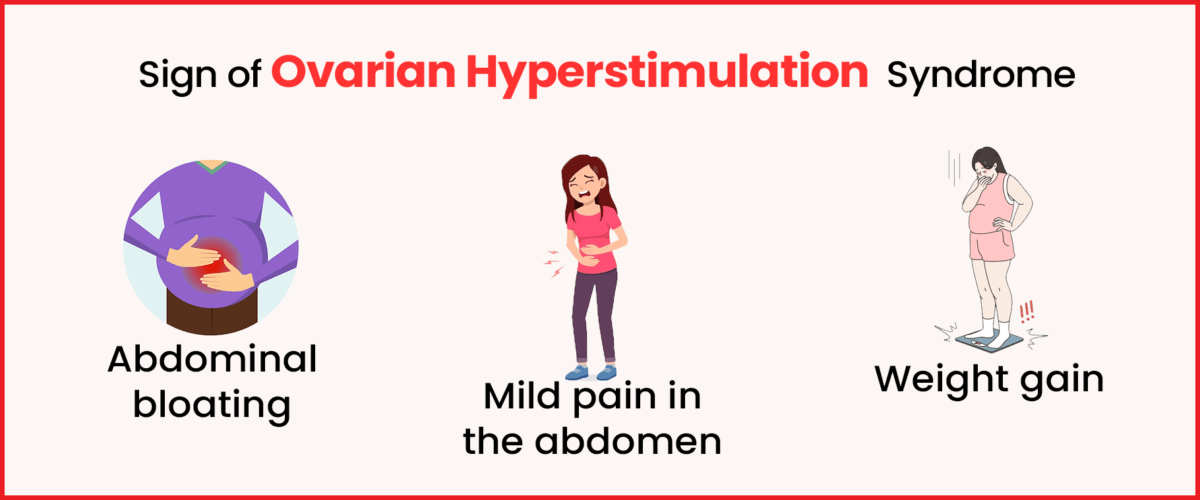
Symptoms of OHSS typically appear within a week of using injectable ovulation-stimulating medications, although they may take longer to manifest. These symptoms vary in severity and can fluctuate over time.
OHSS presents in these categories, determined by symptom severity:
- Mild (Grades 1–2): Characterized by abdominal distention and discomfort, nausea, and diarrhoea.
- Moderate (Grade 3): Exhibits ultrasonographic evidence of ascites, excessive weight gain, increased abdominal girth, vomiting, and diarrhoea.
- Severe (Grades 4–6): Shows clinical evidence of ascites, hydrothorax, and breathing difficulties.
Your healthcare provider assesses the type based on symptom severity. Most OHSS cases are mild, causing temporary discomfort. Severe instances are uncommon but can pose life-threatening risks.
If you’re undergoing fertility treatments and experience symptoms of OHSS, inform your healthcare provider. Even if your case of OHSS is mild, your provider will want to monitor you for sudden weight gain or worsening symptoms.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
If you are undergoing fertility treatment and notice symptoms that could indicate OHSS, it is important to contact your doctor promptly. They will want to examine you to determine if you are experiencing this condition. Some exams your doctor may perform to diagnose OHSS include:
-
Physical Tests:
During physical examination, doctors carefully check indicators like weight gain and belting. The daily scale measurement, the go-to step for diagnosis, will support the conclusion with the rate of weight gain.
By doing so, it becomes apparent how far the severe swelling is going. Analysis of the sample results yields information that allows the doctors to reject or confirm the diagnosis that may be the reason for the observed changes.
-
Ultrasound:
Nowadays, doctors can use imaging equipment, like ultrasounds and X-rays, to find out whether there has been an accumulation of excess fluid inside the body. Patients with OHSS experience excessive water retention, which causes fluid to leak through their blood vessels into the abdominal cavity and the surrounding spaces, resulting in bloating and body aches.
As the amount of fluid increases and starts leaking out of spaces where it was normally held, the symptoms of OHSS gradually worsen. Imaging tests give a doctor the chance to see how much the fluid is enlarging tissues and forcing someone to gain excessive weight.
-
Blood Tests:
Blood tests are often used together with ultrasounds for people undergoing fertility treatment. These medical exams analyze hormone levels, any abnormalities in the blood, and possible kidney problems caused by enlarged, leaking ovaries. If blood tests are part of your regular treatment, early identification of OHSS is more probable. Detecting OHSS sooner can help avoid serious issues. Blood tests measure several vital markers of hormone levels.
Hormone levels indicate how ovaries react to medications designed to stimulate egg growth. Abnormalities in red or white blood cell counts may signal OHSS. Kidney function is also assessed since OHSS can lead to kidney strain if ovaries swell extensively. Together, ultrasounds and blood tests provide doctors with a fuller picture of ovarian health and response to treatment. This helps optimize care and reduce the risks of complications.
Treatment of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
The treatment approach for OHSS depends on the severity of the condition. For mild cases, the primary focus is on ensuring proper fluid intake and monitoring symptoms for worsening.
Mild OHSS may commonly improve independently within around fourteen days. The care concentrates on relieving distress and forestalling issues. Here are some treatments to consider:
- Keeping fluids and electrolytes in balance is crucial to avoid dehydration when the kidneys are damaged. Water or any other fluid intake of 1.5 to 2 litres daily is highly advisable to keep your kidneys in top condition and eliminate any unwanted toxins from your body. Consuming Gatorade or broth restores the right amount of fluids in your body. It is needed to get rid of the excess fluid in your body.
- Adequate sleep plays a significant role in maintaining strong kidneys. To boost your daily activity, follow your doctor’s instructions and try walking, even if just short distances.
- In case of headache or digestion problems, you can use any of the already existing pain relievers to feel more life-like.
Usually, hospitalization or major treatments are not required as long as the patients are stable or their symptoms do not become worse. Nevertheless, in severe cases, an OHSS might have to be hospitalized so that comprehensive medical care can be administered to avoid more serious complications arising. You can resolve these issues with immediate medical consultation.
Plausible and Feasible Treatments may include:
- IV fluids may be administered to replenish fluids and important electrolytes lost through vomiting or diarrhoea.
- If your abdomen has accumulated a sizable amount of fluid, doctors may drain it manually using a syringe, which can potentially provide comfort.
- Other medication will be provided to reduce the activity in the ovary.
Conclusion
OHSS has become the most alarming problem for people with fertility treatments and those using injectable medications for the stimulation of egg production. Appreciating causes, signs, and therapy of OHSS is important as it relates to patients and healthcare providers.
Huge ovarian and abdominal swelling and fluid collection occur because of the over-reproduction of hormonal medications. The impact of that intensive may be mild discomfort or life-threatening complications. Prompt diagnosis using physical exams, ultrasounds, or blood tests is essential to enable the right course of treatment.
Treatment approaches are based on symptom alleviation, which could include fluid intake, adequate rest, pain relief, hospitalization, and intravenous fluid drainage of excess fluid when the case is severe. Close monitoring, communication, and relationships between patients and healthcare professionals mitigate negative outcomes and guarantee the best outcomes during fertility treatment.