Thin Endometrium Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Thin endometrium refers to a condition where the inner lining of the uterus, called the endometrium, is thinner than normal. If the lining is too thin, it may make it a little hard to maintain a full pregnancy. Thin endometrium can be caused by various factors, including age, menopause, endometrial biopsy, radiation therapy, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), and smoking. Treatment options for thin endometrium depend on the underlying cause and may include estrogen therapy, gonadotropins, assisted reproductive technology (ART) procedures, lifestyle changes, and surgery.
Understanding the Thin Endometrium
The endometrium, a crucial layer of tissue lining the uterus, plays an essential thing in the reproductive system of women. Sometimes, this lining may become thinner than optimal, a condition known as thin endometrium. While it may not always manifest noticeable symptoms, there are specific signs that could indicate potential issues. The endometrium is an inner lining that thickens during the menstrual cycle. It consists of different layers, including the basal layer, which contains stem cells that can regenerate the lining, and the functional layer, which thickens and sheds during the menstrual cycle.
Symptoms of Thin Endometrium:
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for women seeking to comprehend their reproductive health.
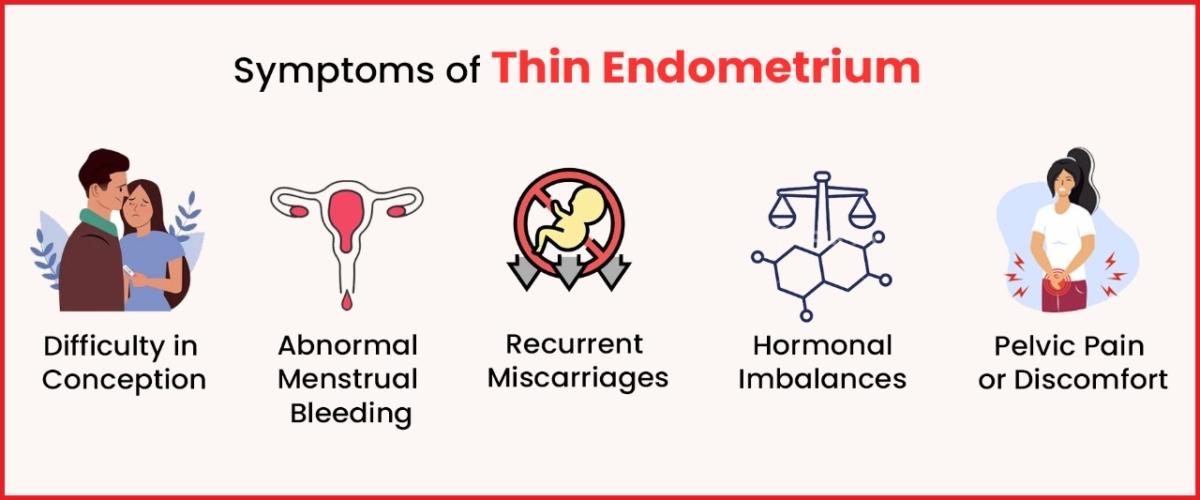
Difficulty in Conception:
One of the primary symptoms associated with a thin endometrium is difficulty in conceiving. The endometrial lining serves as a crucial environment for the implantation of a fertilized egg. If this lining is too thin, it may pose challenges for successful implantation, leading to infertility issues.
Abnormal Menstrual Bleeding:
Women with a thin endometrium may experience irregular and abnormal menstrual bleeding. This can manifest as lighter periods, shorter menstrual cycles, or spotting between periods. These irregularities could be indicative of an insufficiently developed endometrial lining.
Recurrent Miscarriages:
Thin endometrium has been linked to an increased risk of recurrent miscarriages. The inadequate thickness of the endometrial lining may compromise its ability to support a developing embryo, resulting in recurrent pregnancy losses.
Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal imbalances, particularly disruptions in estrogen levels, can contribute to thin endometrium. Women experiencing hormonal irregularities may notice changes in their menstrual cycles, and these imbalances can negatively impact the development of the endometrial lining.
Pelvic Pain or Discomfort:
In a few cases, women with a thin endometrium may experience pelvic pain or discomfort. This may be associated with hormonal fluctuations, compromised blood flow to the uterus, or other factors affecting the health of the endometrial tissue.
Thin Endometrium Causes
The endometrium, a vital layer of tissue lining the uterus, undergoes dynamic changes throughout a woman’s menstrual cycle. However, in some cases, this lining may become thinner than optimal, a condition known as thin endometrium. Understanding the potential causes of thin endometrium is crucial for those facing fertility challenges or recurrent pregnancy loss.
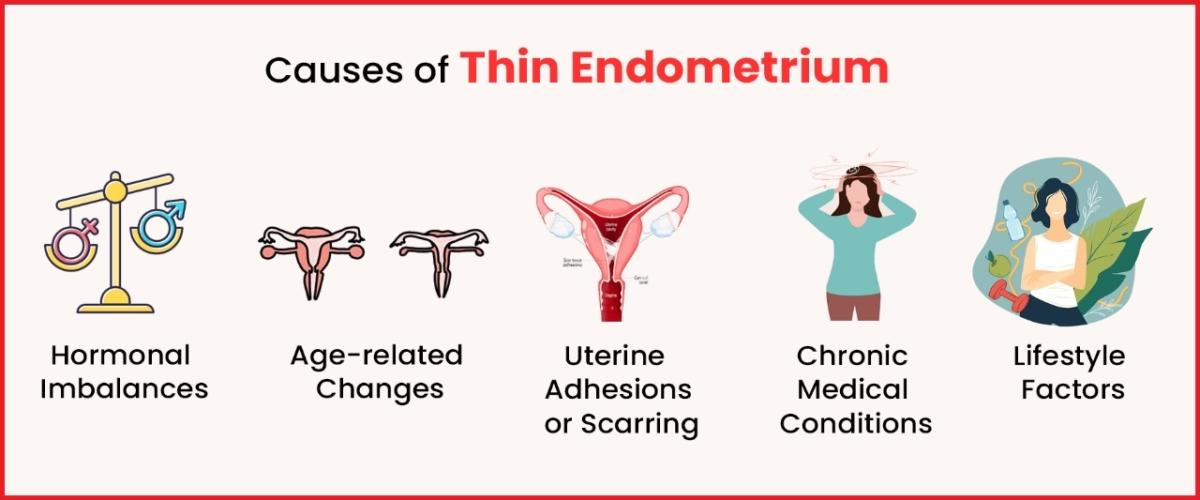
Hormonal Imbalances:
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly imbalances in estrogen and progesterone levels, can contribute to thin endometrium. Estrogen plays a crucial role in promoting the growth and thickening of the endometrial lining. Disruptions in hormonal balance can impede this process, leading to a thinner lining.
Age-related Changes:
Advancing age is a significant factor in the development of thin endometrium. As women approach menopause, hormonal shifts occur, and the ovaries produce fewer hormones. This process can result in a decrease in endometrial thickness and quality.
Uterine Adhesions or Scarring:
Prior uterine surgeries, such as dilation and curettage (D&C) or other procedures, may lead to adhesions or scarring in the uterine lining. This scarring can interfere with the normal growth and development of the endometrium, resulting in thinning.
Chronic Medical Conditions:
Certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, thyroid disorders, or diabetes, can impact endometrial health. These conditions may affect blood flow to the uterus or disrupt hormonal balance, contributing to thin endometrium.
Infections or Inflammation:
Infections or chronic inflammation of the uterus can hinder the normal regeneration of the endometrial tissue. Conditions like chronic endometritis, an inflammation of the endometrium, may lead to thinning of the lining over time.
Lifestyle Factors:
Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or extreme stress, can negatively impact reproductive health. These factors can contribute to hormonal imbalances and reduce blood flow to the uterus, affecting endometrial development.
Poor Blood Flow to the Uterus:
Insufficient blood flow to the uterus can impede the nourishment and growth of the endometrial tissue. Conditions such as vascular abnormalities or uterine artery embolization may compromise the blood supply, resulting in a thin endometrium.
Thin endometrium is a complex condition with various potential causes. Recognizing these factors is crucial for individuals facing fertility challenges or recurrent pregnancy loss. Consultation with a healthcare professional is essential for a comprehensive assessment, diagnosis, and development of a personalized treatment plan to address the specific causes and improve endometrial health. Early detection and targeted interventions can significantly enhance the successful conception and a healthy pregnancy.
Treatment for Thin Endometrium
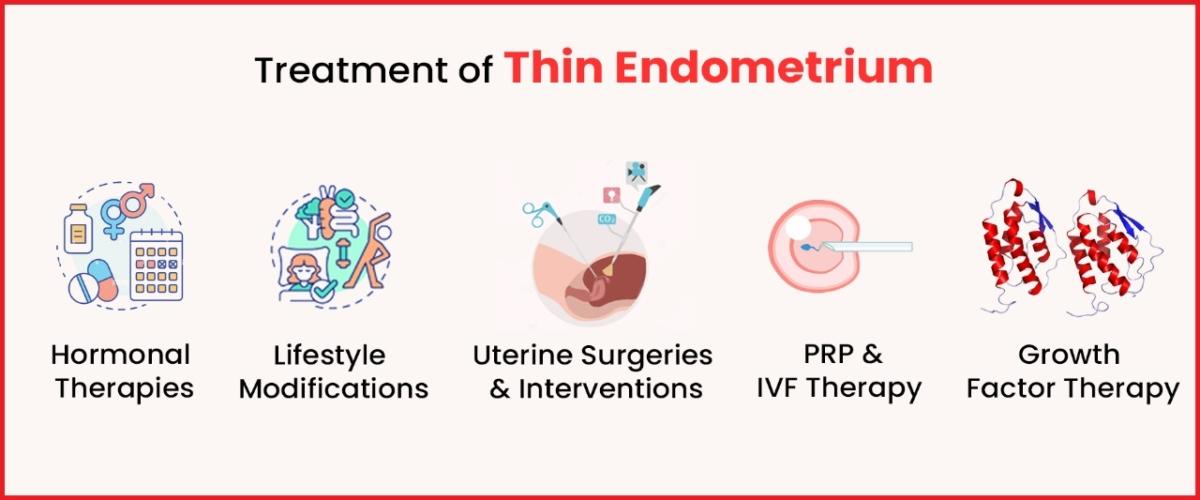
Thin endometrium, characterized by a suboptimal thickness of the uterine lining, can present challenges for women trying to conceive. However, advancements in reproductive medicine have led to various treatment approaches aimed at improving endometrial health. This article explores the key strategies employed in the treatment of thin endometrium, offering hope to those seeking to enhance their fertility.
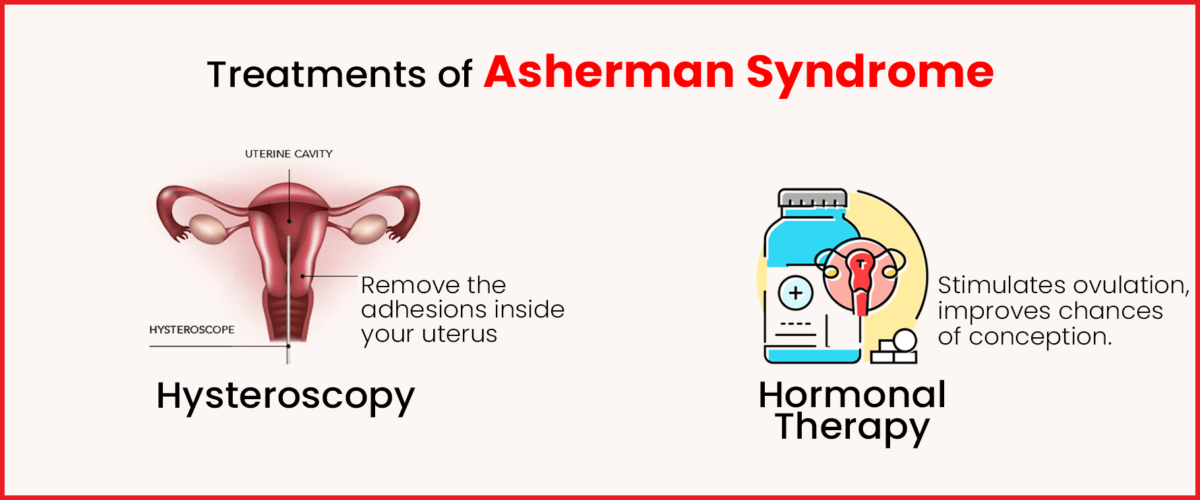
Hormonal Therapies:
Hormonal interventions are often employed to address thin endometrium. Estrogen, a hormone crucial for endometrial growth, may be administered in different forms, such as oral medications, patches, or injections. Additionally, progesterone supplementation may be prescribed to support the second phase of the menstrual cycle and facilitate a healthy endometrial response.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can positively impact endometrial health. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle changes contribute to overall reproductive well-being and may promote the development of a thicker endometrial lining.
Uterine Surgeries and Interventions:
In cases where structural abnormalities or scarring contribute to thin endometrium, surgical interventions may be considered. Procedures such as hysteroscopy can be used to remove adhesions or address underlying issues affecting the uterine lining. These interventions aim to create a more favourable environment for endometrial growth.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
Emerging as a promising option, PRP therapy involves injecting platelet-rich plasma, derived from the patient’s blood, into the uterine lining. Rich in growth factors, PRP stimulates tissue regeneration and improves blood flow, potentially enhancing endometrial thickness.
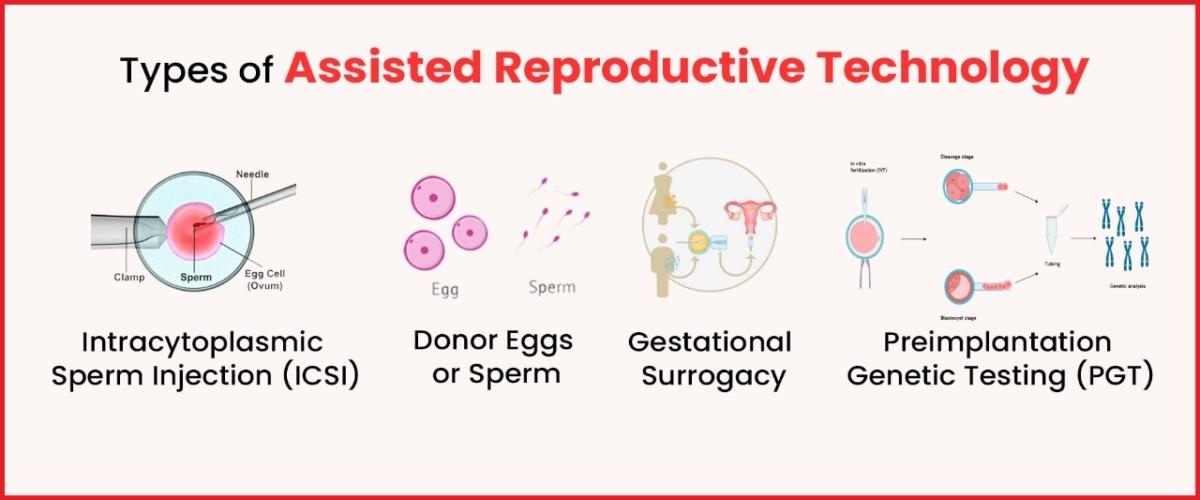
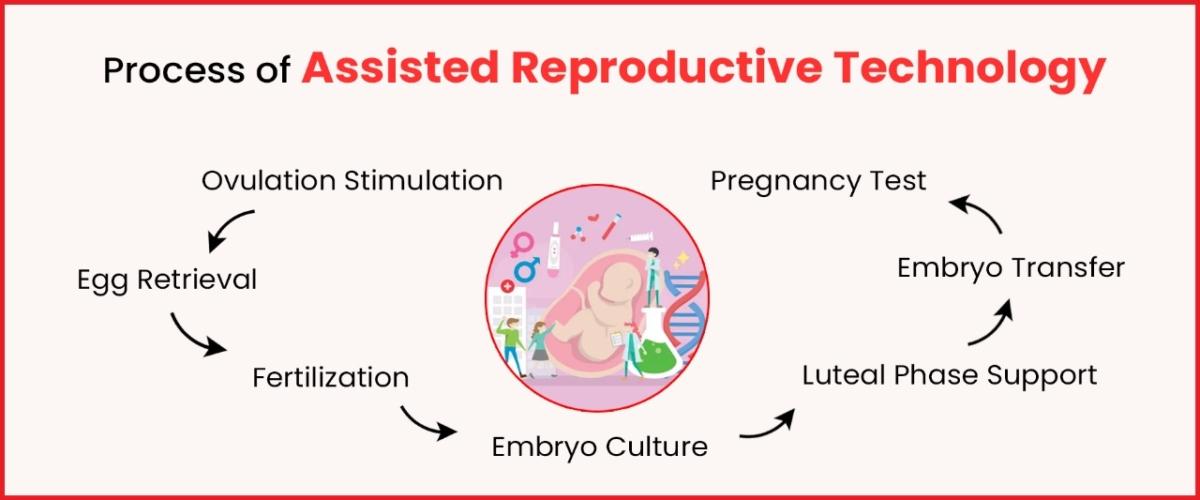
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) with Embryo Glue:
For couples undergoing assisted reproductive technologies like IVF, the use of a specialized embryo transfer medium known as “embryo glue” has been explored. This medium contains substances that may aid in better embryo attachment to the thin endometrial lining, potentially improving implantation rates.
Acupuncture and Traditional Chinese Medicine:
Some individuals turn to acupuncture and traditional Chinese medicine as complementary approaches to enhance endometrial thickness. Acupuncture is believed to improve blood flow to the uterus and regulate hormonal balance, potentially creating a more supportive environment for endometrial growth.
Growth Factor Therapy:
Research is ongoing in using growth factors, such as granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), to promote endometrial regeneration. Preliminary studies suggest that these factors may stimulate tissue repair and improve endometrial thickness.
The treatment landscape for thin endometrium is diverse, reflecting the complexity of the condition. Individualized care plans, tailored to address specific causes and patient needs, are essential. Consulting with a fertility specialist is crucial for a comprehensive evaluation and the development of a personalized treatment strategy. With advancing medical interventions and a holistic approach, there is optimism for individuals facing the challenge of thin endometrium to realize their dreams of conception.
Conclusion to Thin Endometrium
Thin endometrium can be a challenging condition for women who are trying to conceive. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, it is possible to improve endometrial health and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy. If you are having difficulty conceiving, it is important to talk with your IVF experts and develop an appropriate treatment plan. If you are looking for any treatment like this then you can consult any of the best organisations like Imprimis. They will help you to get fully recovered at reasonable prices.